ESG Reporting (Environmental, Social and Governance) is an increasingly important tool for businesses to assess and transparently demonstrate their performance in three areas: Environment, Social and Governance. ESG reporting not only benefits businesses but also contributes to sustainable development for communities and society.
1. What is ESG Reporting?
ESG reporting is the publication of information on a company's sustainability factors according to ESG (Environment, Social, Governance) criteria. The ESG reporting process includes activities such as analyzing, selecting indicators, measuring, aggregating, and reporting on the material information of the three ESG pillars.
2. The Importance of ESG Reporting
Attract green investment capital
ESG reporting helps businesses increase transparency, helping investors and stakeholders assess a company's performance and potential for sustainable development.
Enhance the company's image
According to a 2022 Intexlex survey, 74% of respondents believe that ESG is a key factor influencing a company's performance and reputation. ESG reporting has both direct and indirect impacts on a company's recognition and reputation.
Foundation for a company's sustainable development roadmap
- Comply with legal and ethical business practices
- Effective risk management and supply chain optimization
- Maintain a competitive advantage
3. ESG Standards
ESG standards are tools to assess a company's ESG practices based on their commitments and actions to protect the environment and minimize negative environmental impacts. This is the basis for identifying socially responsible companies. Businesses will report their ESG practices based on sustainability reporting frameworks.
The three main pillars of ESG standards:
3.1. Environmental (E) aspect: Assesses the company's impact on the environment, including natural resource use, emissions, pollution, and climate change.
- Climate change: Companies are assessed based on the amount of greenhouse gas (GHG) missions from their business operations. This is based on a company's commitments and actions to reduce GHG emissions and adapt to climate change.
- Energy: ESG will assess a company based on its energy consumption per unit of product or service, the proportion of renewable energy used in total energy consumption. Or use natural energy sources such as wind,... to minimize energy depletion.
- Natural resources: To achieve a high ESG score in this area, a company must have full licenses for the natural resources it uses. At the same time, take practical actions to restore polluted areas, or research and deploy new technologies to self-generate resources.
- Waste treatment and recycling: This is measured based on the type of waste generated from the company's business operations, including hazardous waste, domestic solid waste, medical waste, etc. Along with that, the company's waste management methods such as reuse, recycling, composting, incineration, etc.
3.2. Social (S) aspect: Assesses the company's social responsibility, including business ethics, working conditions, employee rights, occupational safety, social responsibility and community.
- Privacy and security: To implement this criterion, the company must ensure that it does not disclose personal information and must commit to protecting the data of its members. They must ask for their consent before collecting and using personal data for common purposes.
- Diversity, equity and inclusion: Based on the Labor Code, ESG will assess a company based on diversity of gender, age, race, religion, etc. in the company's workforce. In particular, businesses must not discriminate on the basis of gender and all are treated fairly in all aspects.
- Safe working environment: Businesses need to assess and control environmental risks that can affect the health and safety of workers, such as environmental pollution, noise, etc. At the same time, comply with occupational safety regulations, provide adequate protective equipment for workers, etc.
- Working conditions: ESG will assess a company based on Vietnamese law on the extent to which it ensures the rights of workers such as wages, working conditions, occupational safety, social insurance, etc.
3.3. Governance (G) aspect: Assesses the effectiveness of a company's governance, including information transparency, governance structure, accountability, business ethics, and anti-corruption.
- ESG reporting: Businesses that follow ESG standards need to publicly disclose information with financial reports, business performance results, labor policies,...
- Anti-bribery and corruption: Businesses need to be open and transparent in their governance and operations, not accepting bribes from subordinates,... ESG will be assessed according to the Anti-Bribery & Corruption Law - Vietnam's Criminal Law.
- Diversity and inclusion of the board of directors: This ESG criterion assesses the diversity of origin of the members of the board of directors in terms of gender and background.
4. ESG Reporting Frameworks
Several popular sustainability reporting frameworks are available for businesses to consider using:
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Reporting Framework: Established in 1997 by Ceres and the Tellus Institute, with support from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- GRI is the official reporting standard of the United Nations Global Compact.
- GRI is the default reporting framework for over 5,800 reporting methodologies and is widely recognized as the global standard for ESG reporting.
- GRI takes a comprehensive approach to ESG issues with equal importance to environmental, social, and governance factors. The GRI Standards include: 3 Universal Standards that apply to all organizations and businesses; 33 Standards that address specific content and are organized into three groups: Economic, Environmental, and Social. Organizations and businesses select and use only the relevant Standards based on their material topics.
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): Established in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB).
- The TCFD Recommendations have been widely adopted by companies and financial institutions around the world.
- Over 10,000 companies and financial institutions have reported according to TCFD.
- TCFD focuses on the financial risks and opportunities of climate change for businesses, covering four thematic areas: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, and Metrics.
Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP): Founded in 2009 and headquartered in London, UK. CDP is considered by the global economy to be the gold standard for environmental reporting, with the most extensive and comprehensive database of greenhouse gas emissions and energy use data in the world.
- The CDP community consists of over 8,400 participating organizations, creating an environment for sharing experiences, learning from each other, and collectively improving ESG reporting effectiveness.
- CDP focuses on the "Environment" with a focus on addressing the "Governance" aspect related to issues such as Climate, Water, and Forests.
Other Standards:
- GHG Protocol Standards for Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) Standards
- International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) Framework
5. ESG Ratings
ESG Ratings (Environmental, Social and Governance) are a tool for measuring a company's sustainability performance based on three criteria: Environment, Social, and Corporate Governance.
Each criterion has its own evaluation and scoring system, which is aggregated into an "ESG Score". The ESG Score is a transparent measure of an organization's commitment to sustainable development and its ability to create long-term sustainable value.
5.1 Importance of ESG Ratings
Easier access to green capital: A high ESG rating indicates a transparent, low-risk, and reputable company. Therefore, an ESG score helps businesses receive investment opportunities from doing well in governance and operations, generating sustainable and long-term profits.
Enhanced brand image: Consumers are increasingly aware of sustainability issues and prioritize purchasing from brands that are socially and environmentally responsible. Businesses with high ESG scores will create goodwill, build trust and loyalty with consumers, and attract more customers. According to a McKinsey study (February 2023), over 60% of consumers are willing to pay more for a product with "eco-friendly" packaging.
Attract talented personnel: Businesses with high ESG scores can easily attract potential employees. This is because the ESG score reflects the quality of the work environment and the company's policies. Employees will be willing to contribute and stay with the company for the long term.
5.2. Common ESG Scoring Methods
Qualitative method: ESG rating organizations collect data through surveys, combined with other data sources (government, press, etc.) to synthesize, analyze, calculate, and provide the most accurate results. The strength of this method is its objectivity, based only on the list of sustainable development indicators and not influenced by personal opinions.
Quantitative method: ESG rating organizations collect data through ESG reports and financial reports from businesses. The strength of this method is time savings, but using only data from businesses can reduce objectivity.
5.3. Some ESG Rating Organizations
Sustainalytics: Owned by Morningstar, a leading financial services provider. Sustainalytics evaluates thousands of companies worldwide across a wide range of industries, providing deep insights into companies' sustainability performance and ESG-related risks.
MSCI: Rates over 13,000 companies (including subsidiaries) and over 650,000 equity and fixed income securities globally. MSCI is used by 46/50 of the world's top asset management firms.
CDP: Over $110 trillion in assets are rated annually, and over 200 companies, spending over $5.5 trillion annually on procurement, have required their partners to disclose environmental data in accordance with CDP ratings.
S&P Global: S&P Global, through its index division, offers a variety of ESG-focused indices, including the S&P 500 ESG Index. This is a centralized source of S&P Global solutions, combined with Trucost's environmental data to provide comprehensive insights and tools for businesses to assess ESG risks and opportunities.
6. Real-world ESG practices in Vietnam
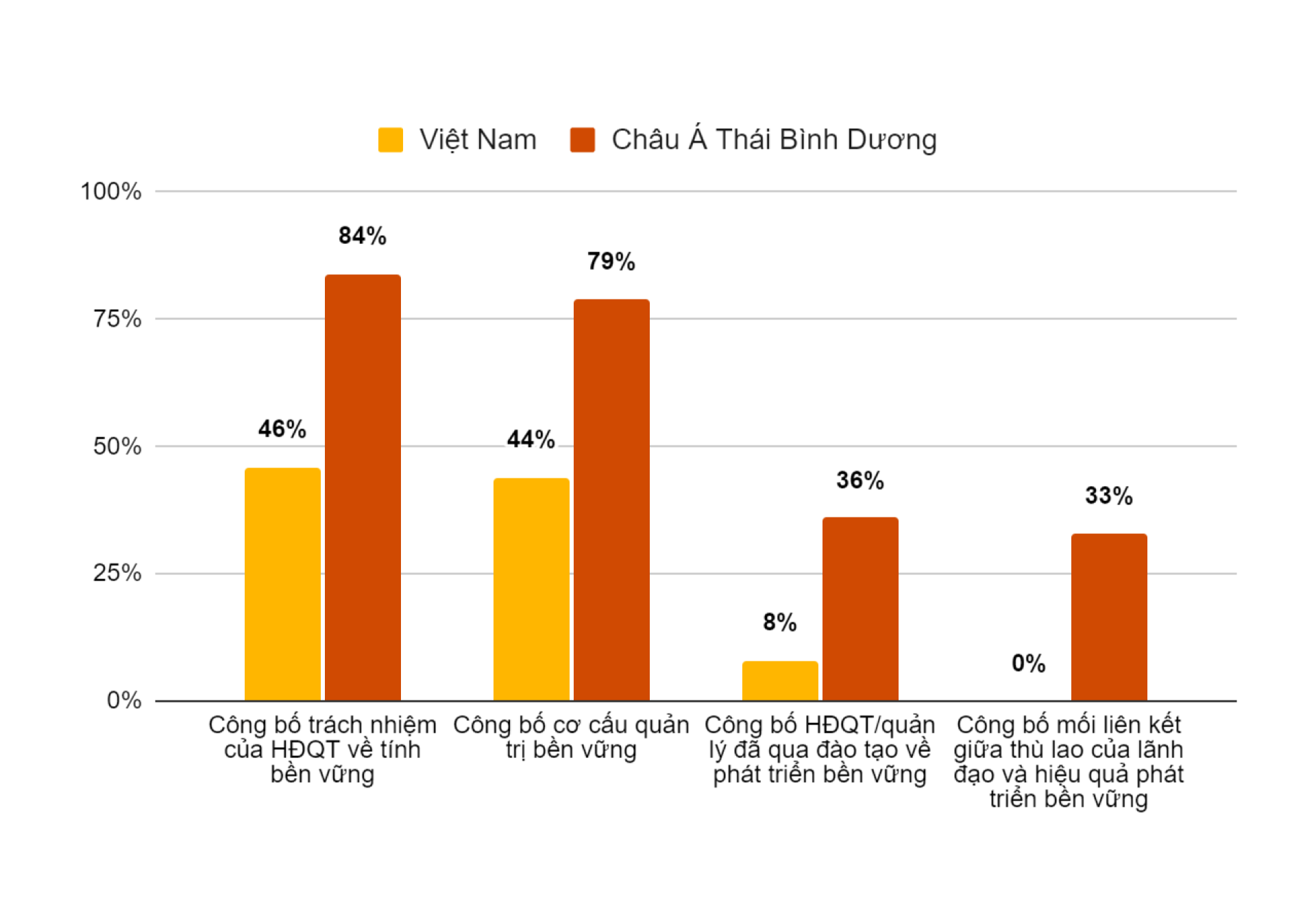
The Current State of ESG Implementation by Businesses in Vietnam and Asia Pacifi
According to a 2022 report on the readiness to implement ESG in Vietnam by PwC (one of the four leading auditing firms in the world today), up to 80% of businesses have made commitments or plan to implement ESG in the next 2-4 years. Of which, 57% of FDI enterprises have built clear ESG commitments. 58% of listed companies in Vietnam said they plan to commit to ESG in the near future. In addition, 40% of private/family businesses surveyed said they have made ESG commitments.
Most businesses in Vietnam prioritize the Governance (G) factor in their implementation program with 62% choosing, followed by the Environment (E) factor with 22% and the Social (S) factor with 16%.
Related articles:
GIANT BARB SCIENCE AND ENVIRONMENT JOINT STOCK COMPANY
📞 Hotline: +84 983 700 168
✉️ Email: info@giantbarb.com
🏢 Headquarter: No.07 Ton That Thuyet, Dich Vong Hau ward, Cau Giay district, Ha Noi